NEW YORK (CNN/Money) -
The American consumer has become deeply addicted to spending, running up ever higher levels of debt in order to live in a fashion that is beyond his means. And the world has become equally addicted to the consumer continuing to burn through cash.
It's a dangerous situation -- potentially a bubble that dwarfs even the U.S. asset bubble that burst in 2000 -- and it will be a challenge for policy-makers to keep it from ending badly.
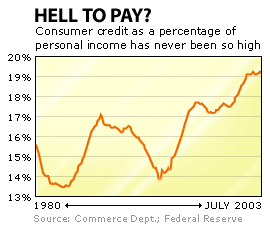
The perseverance of consumer spending over the past several years is credited with keeping the economy afloat, but it didn't come without consequence. In order to keep on living in the manner they became accustomed to during the boom years, Americans went deeply into hock.
"If there's a bubble, it's in this four-letter word: Debt," said Merrill Lynch chief North American economist Dave Rosenberg. "The U.S. economy is just awash in it."
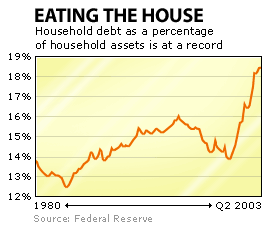
Indeed, consumer credit and mortgage debt are both a higher percentage of disposable income now than they've ever been before. Nor do these rises in debt levels appear justified by the rise in the value of people's homes -- household debt as a percentage of household assets (what you owe versus what you're worth) has also never been so high, according to the Federal Reserve.
How did this come to pass? We live in an economy that has become deeply dependent on the American consumer for growth. U.S. consumer spending accounts for around 70 percent of U.S. gross domestic product. So nobody wants to see the consumer falter, and they have been doing their darndest to make sure that doesn't happen.
The Federal Reserve has cut rates like never before, allowing mortgage rates to come down this year to their lowest recorded levels. Car companies have offered zero percent financing for two years now, and they've recently begun offering it on 2004 vehicles.
But rather than using such rate reductions as an opportunity to save money, consumers have, as a whole, used them as an opportunity to spend more.
"We're a what's-my-monthly-payment nation," said Northern Trust chief U.S. economist Paul Kasriel. "The idea is to have my monthly payments as high as I can take. If you cut interest rates, I'll get a bigger car."
 |
|
| Use your home equity loan to buy this $10,000 mermaid suit! |
Financial companies have got into the act, too, offering people ever-more efficient ways of running up debt. Hardly does a week go by without a new credit card offer coming in the mail.
Or consider credit cards like Wells Fargo's NowLine Visa Platinum, which allows you easy access to a home equity line of credit. You can use it, says Wells in its online promotion, to help pay "for everyday expenses, like gas, groceries, clothes, etc."
Eating your house was never so easy.
Codependency, anyone?
Other countries share in the deep commitment to keep U.S. consumers laying out their cash. Big exporters -- Japan and China in particular -- have strived to keep their currencies low against the dollar, allowing Americans, in effect, to buy more of their stuff. U.S. consumer spending accounts for around 20 percent of world gross domestic product.
But here is another situation where the United States is spending more than it makes. The current account deficit -- the gap in the United States' trade in goods and services with the rest of the world -- has risen to about 5 percent of the total economy. That's as high as it's ever been. The chart of the current account gap as a percentage of GDP, incidentally, looks almost exactly like a chart of consumer credit as a percentage of income.
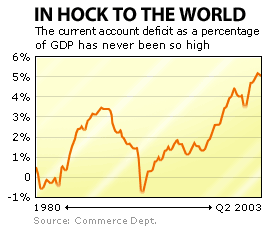
So the world economy is leveraged to the U.S. consumer. And the U.S. consumer is leveraged to the hilt. There are now more registered cars on the road in the United States than there are licensed drivers. America's energy needs, per capita, are nearly twice that of Great Britain's. At some point the U.S. consumer's creditors -- which is to say the rest of the world -- may have second thoughts about how their money is being used. Kasriel compares it to a corporation that uses its stock and bond proceeds to throw big parties, rather than invest them in its future.
Clearly something has to give.
"Nobody can pinpoint when this process will come to an end," said Carlos Asilis, a portfolio manager with the hedge fund Vega Capital Management. "But it is very clear that it can't go on forever. Do you let this bubble grow, or do you do something about it?"
There are signs that U.S. policy-makers are at least partially trying to address the problem, pressing Japan, China and other Asian exporters to let their currencies strengthen against the dollar. This would, they believe, reduce consumer expenditures on imported goods and fuel export growth as well.
But it might not solve the problem of consumers who are continuing, in effect, to eat their seed corn. It would take a powerful disincentive, like a Fed rate hike, to get people to stop spending and start paying down debt and save more. But to do that would be to court the forces of recession.
"We have a Fed that wants a booming economy, but the only way the consumer can continue to fuel the economy is through continued debt accumulation," said Rosenberg. "I don't know if there's an easy way out."

|

